„Ärztliche Stelle of the Bundeswehr“ National and International
Aus der Unterabteilung VI des Kommando Sanitätsdienst der Bundeswehr, Koblenz (Unterabteilungsleiter: Oberstarzt Dr. Th. Harbaum) und aus dem Institut für Präventivmedizin der Bundeswehr, Andernach (Leiter: Oberstarzt Prof. Dr. Dr. D. Leyk)
Abstract – The National and International Medical Quality Control Board of the Bundeswehr named „Ärztliche Stelle of the Bundeswehr“ is responsible for the quality assurance program according to the German Radiation Protection Law. This includes nuclear medicine and radiological institutions.
The challenge is to equally maintain the criteria for the association`s body medical self-administration and autonomy considering National and International Operations of the Bundeswehr and to provide the legal framework from the Radiation Protection Regulations simultaneously.
The German central conference of federal states for clinical audit in Radiation Protection implemented a standardized evaluation system. These regulations build the basis for the work of the „Ärztliche Stelle of the Bundeswehr“, which has already achieved quality improvement in nuclear and x-ray medical diagnostics and therapy.
Key words: Ärztliche Stelle of the Bundeswehr; Medical Quality Control Board; Supervisory Center for Medical Radiation Protection; National and International Operations of the Bundeswehr
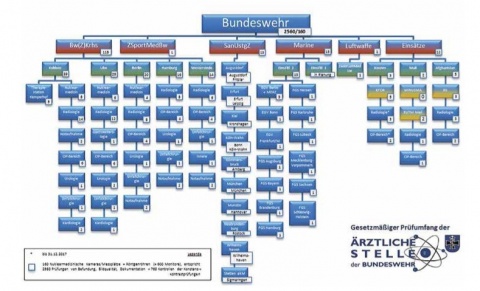
Zusammenfassung – Für die Qualitätssicherung bei der Anwendung radioaktiver Stoffe und ionisierender Strahlung am Menschen in Einrichtungen der Bundeswehr ist gemäß Strahlenschutzgesetz (vormals Atomgesetz) und Strahlenschutzverordnung das Nationale und Internationale Medizinische Qualitätskontrollgremium der Bundeswehr mit dem Namen „Ärztliche Stelle der Bundeswehr“ zuständig. Zu den zu kontrollierenden Einrichtungen zählen sowohl Nuklearmedizinische Abteilungen und Kliniken in den Bundeswehrkrankenhäusern als auch Röntgeneinrichtungen in den Bundeswehrkrankenhäusern, Facharztzentren, Schiffen der Marine, im Zentrum für Luft- und Raumfahrtmedizin der Luftwaffe, im Zentrum für Sportmedizin der Bundeswehr sowie in medizinischen Einrichtungen der Auslandseinsätze.
Eine Herausforderung der „Ärztlichen Stelle der Bundeswehr“ besteht darin, unter Wahrung der Kriterien eines Organs der ärztlichen Selbstverwaltung und unter Berücksichtigung der nationalen und internationalen Einsätze der Bundeswehr, gleichzeitig den rechtlichen Rahmen des Strahlenschutzgesetzes einzuhalten bzw. zu schaffen.
Die deutsche zentrale Vereinigung (ZÄS) aller nach Landesrecht und vom Bund bestimmten Ärztlichen Stellen für Nuklearmedizin, Röntgen und Strahlentherapie hat ein standardisiertes Bewertungssystem zur strahlenschutzrechtlichen Qualitätsprüfung implementiert. Dieses Qualitätsmanagementtool bildet die Grundlage für die Tätigkeit der „Ärztlichen Stelle der Bundeswehr“, die bereits eine Qualitätsverbesserung in der nuklearmedizinischen Diagnostik und Therapie sowie der Röntgendiagnostik erreichen konnte.
Schlüsselwörter: Ärztliche Stelle der Bundeswehr; Medizinische Qualitätskontrolle; Zentrum für medizinischen Strahlenschutz; Nationale und internationale Einsätze der Bundeswehr
Introduction
Medical imaging and interventional procedures requiring ionizing radiation or radioactive substances are frequently used in diagnostic and therapeutic management of patients.Over the last 25 years, there has been a steady increase in the use of diagnostic and interventional high dose x-ray examinations, nuclear medicine procedures and radiotherapy treatments (Hricak and Dauer 2017).
Monitoring of patient dose is important to keep irradiation time as short as possible to achieve patient protection. By verification acute tissue reactions can be avoided and stochastic effects such as radiation-induced carcinogenesis can be minimized (Beyreuther 2009; Wilson-Stewart 2017).
The National and International Medical Quality Control Board of the Bundeswehr named „Ärztliche Stelle of the Bundeswehr“ is responsible for the quality assurance program according to the German Radiation Protection Ordinance and the X-Ray Ordinance.
This includes Quality management which includes both Quality assurance and Quality control of radiation dose reduction for patients undergoing nuclear medicine diagnosis and therapy, diagnostic and interventional radiology, and medical research. “Ärztliche Stelle of the Bundeswehr” audits verify whether the performed medical examinations conform to the requirements and principles of Quality management have been implemented in the department (Heidenreich 2005; Ertl-Wagner 2011; Hahn 2015).
Quality assurance and Quality control are dependent on each other. The purpose of Quality assurance is to prevent unnecessary radiation doses as a proactive quality process, whereas Quality control identifies a lack of radiation protection as a reactive process.
Legal Basis
Beginning in 2019 the Supervisory Center for Medical Radiation Protection will have the following pyramid of legal basis with the Radiation Protection Law, followed by the German Radiation Protection Ordinance (the X-Ray Ordinance will then be included by the Radiation Protection Ordinance) and Regulations of the Federal Ministry for the Environment, Nature Conservation, Building and Nuclear Safety and the Federal Office for Radiation Protection as well as Recommendations of the German Commission on Radiological Protection (Richter 2015; RL RöV, StrlSchV 2015).
Tasks
Reducing patient dose, avoiding unnecessary radiation exposures and minimizing the risk of accidents are the major goals of Radiation Protection and safety of patients (Heidenreich 2005; EURADOS Annual Meeting 2008; EANM, EFOMP, EFRS, ESR, ESTRO 2017). The principal task of the “Ärztliche Stelle of the Bundeswehr” is the supervision of compliance via legal regulations to achieve optimal protection of patients from the hazards of ionizing radiation (Ertl-Wagner 2011; Piotrowski 2013; Hahn 2015). This includes the following fields:
Justifying indication
The “Ärztliche Stelle of the Bundeswehr” has to verify the justification for radiation exposure by considering the balance of health benefit against the radiation risk for the patient, taking all circumstances of individual cases into account. Appropriate criteria for radiation protection should include imaging referral guidelines and ethical considerations as tools to analyze the justification and to ensure that patients referred for radiation exposure examinations really need the procedures.
Medical science
The Medical Quality Control Board has to check whether the requirements of medical science are performed in diagnostic and therapeutic radiation applications.
Medical research
One of the tasks of the Medical Quality Control Board is the verification of applications in the context of medical research in accordance with § 23 German Radiation Protection Ordinance and § 28a X-Ray Ordinance regarding studies that include radiation exposure procedures.
Diagnostic reference levels
In 2002, diagnostic reference levels in x-ray diagnostics were introduced for the first time in Germany by the revision of the X-Ray Ordinance. The “Ärztliche Stelle of the Bundeswehr” is required to review compliance for x-ray diagnostic and nuclear medicine procedures using dose reference levels published by the Federal Office for Radiation Protection. Dose reference levels are defined as dose values. These values indicate whether the patient dose for a special imaging procedure is unusually high or low (Schäfer et al. 2014).
Radiation absorbed dose
Unnecessary radiation exposure should be avoided (Neves et al. 2012). The Board has to verify that the radiation absorbed dose to the patients is kept as low as reasonably achievable (ALARA principle). In cases of therapy, an individual dose calculation needs to be performed. The aim is to reduce doses while keeping quality high.
Therapeutic nuclear medicine applications
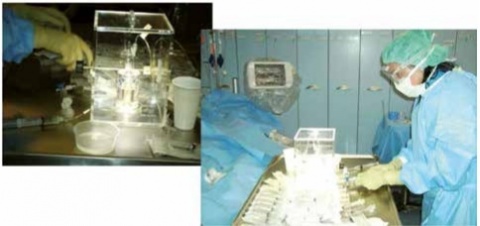
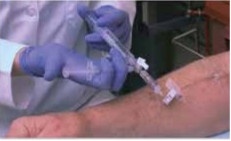
The primary principle of nuclear medicine therapeutic procedures relies on an accurate diagnosis of the tumor region combined with an optimal treatment planning and the precise localization of the target volume (for example Selective Internal Radiation therapy with yttrium-90 for unresectable liver tumors; Abb. 2). Over- as well as undertreatment of patients must be avoided.
All of these test criteria have to be verified by the Supervisory Center for Medical Radiation Protection.
Quality standards
The verification that the required quality standards for medical radiation procedures are performed during examinations and treatments represents a further task of the Medical Control Board, that has to ensure high and consistent quality standards of practice for the medical services of the Bundeswehr worldwide.
Technical equipment and technical maintenance
Imaging technology and its maintenance play an important role for patients` radiation exposure and for image quality (Hanibali 2009; Keevil 2014). The Board has to check special test criteria for verification of the technology, considering state-of-the-art technology (Kopp 2015). In special cases nuclear medicine institutions have to replace old cameras by new ones, especially if the procedure performed by the old camera could cause substantial harm to the patients.
Technologists can decrease the radiation exposure dose to the patient (Van Dyk 2008; Christofides 2013; Rentetzi 2017), for example by widening the energy window. But the increase of scatter, which reduces the contrast of imaging, must also be considered.
Optimization
Optimization should follow the justification. Consultation and recommendations on optimization measures in diagnostic and therapeutic radiation applications are tasks of the Medical Quality Control Board. The aim is to minimize radiation exposure for the patient while conserving high standard image quality.
Medical experts instructions
Developing and implementation of medical expert instructions, as well as guidelines and decrees for the Ministry of Defense (BMVg) represents a further task of the “Ärztliche Stelle of the Bundeswehr” as a federal authority.
Military-civilian Cooperation
The Cooperation of the Center for Medical Radiation Protection with the civilian Centers for Medical Radiation Protection of the federal states and the Special Committees for Radiation Protection and for Nuclear Energy is very important for networking, when establishing clinical audits. Especially, the cooperation between authorities and professionals will enable a development of a radiation safety culture.
Documentation and Archiving
The Board has to review the records that contain the indications for radiation exposure.
The verification of the documentation, that female patients are not pregnant or breastfeeding or that scans on children were performed with special filters or that treatment errors, such as treatment of the wrong does not occur (Richardson 2012), has to be performed (Neves et al. 2012).
Information of the Ministry of Defense
In cases where the diagnostic reference values are exceeded or the recommendations of the Center for Medical Radiation Protection are disregarded, the Board has to inform to the Ministry of Defense. In the event of possible danger to the patient, the incident must be reported immediately.
Places of inspection in Germany and International Operations
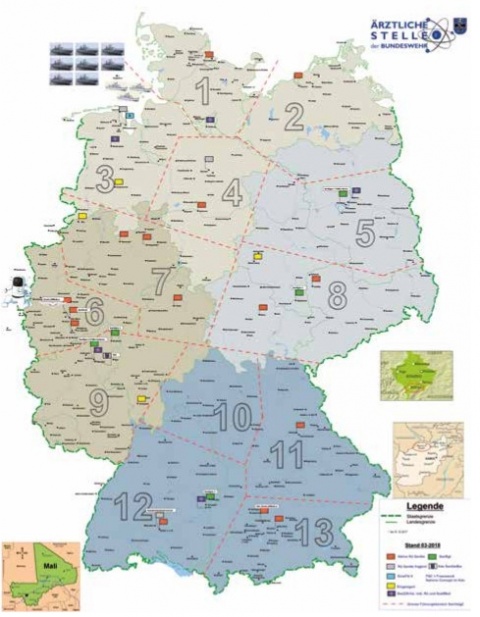
The medical radiation exposure institutions of the Bundeswehr are spread worldwide. These are the Military Hospitals, medical specialist centers, the Federal German ships, the German Air Force Center for Aerospace Medicine and the International Operations. Figure 4a and 4b shows the location of the Inspection facilities for the “Ärztliche Stelle of the Bundeswehr”.
International Operations
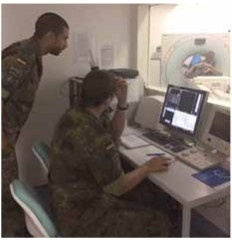
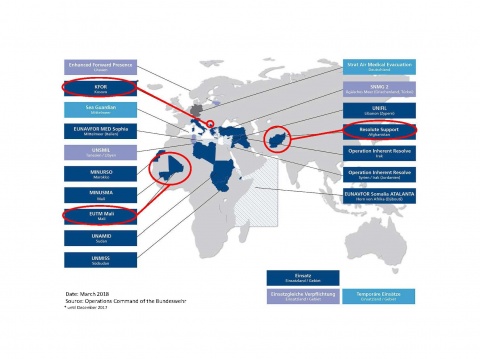
Especially in the military field of foreign countries, the “Ärztliche Stelle of the Bundeswehr” is very interested in considering lessons learned from other nations as take home messages. In return the Bundeswehr shares its experience in radiation protection and its expertise in qualified control of medical radiation exposure with foreign nations.
Standardized Evaluation System
The German central conference of federal states for clinical audit in Radiation Protection is a platform for communication and information of all German federal states. These conferences take place twice a year. Their members are the heads of the “Ärztliche Stellen”. For quality assurance, a standardized evaluation system has been implemented, which builds the basis for the work of every German „Ärztliche Stelle” within the states as well as the „Ärztliche Stelle of the Bundeswehr“ (Lang 2015).
Summary and outlook
Introduction of medical procedures like x-ray examinations, nuclear medicine procedures and radiotherapy treatments have improved patients’ outcome.Since the absorbed dose of radiation to the patients has to be kept as low as reasonably achievable, Boards for verification of the risk : benefit ratio had to be established. The Board members are required to have knowledge and experience in the field of Radiation protection.
The German Institutions of federal states that check the quality of medical application of ionizing radiation and radioactive substances are named “Ärztliche Stellen”.
Every German federal state has established its own Medical Quality Control Board. For the Bundeswehr a separate Board was established by considering its special military field.
The challenge for the „Ärztliche Stelle of the Bundeswehr“ is to guarantee the criteria for the association`s body, medical self-administration, and autonomy considering National and International Operations of the Bundeswehr at the same time as to provide the legal framework for Radiation Protection Regulations.
The „Ärztliche Stelle of the Bundeswehr“, established in 1994, has achieved quality improvement in nuclear and x-ray medical diagnostics and therapy. By the use and continued refinement of all verification tools, the Center for Medical Radiation Protection will enable further significant reduction of patient dose for medical radiation exposure procedures in the future.
(Literature by the author)
(Figure source: Bundeswehr Medical Service Headquarters and Department of Nuclear Medicine, Bundeswehr Central Hospital Koblenz).
Lieutenant Colonel (MC)
Dr. med. Manuela A. Hoffmann
Head of the Supervisory Center for Medical Radiation Protection
Medical Specialist in Nuclear Medicine
Bundeswehr Medical Service Headquarters
Von-Kuhl-Straße 50, 56070 Koblenz
E-Mail: [email protected]
Datum: 17.09.2018
Quelle: Wehrmedizin und Wehrpharmazie 2/2018